Analysis of the development history of Japanese industrial robot industry
At the end of the 1960s, the Japanese economy was in a period of rapid development, with an average annual growth rate of 11%. The rapid economic development also exacerbated the difficulty of the Japanese labor force. In 1967, Kawasaki Heavy Industries of Japan introduced robots and their technology from the United States, and in 1968 developed the first Japanese-made "Unimate" robot.
After a series of processes of digestion, absorption and innovation, Japanese industrial robots quickly entered the practical period of the 1970s from the cradle of the 1960s. In 1980, it was called Japan's "first year of robot popularization". Japan began to promote the use of robots in various fields. 1980-1991 was the first boom of the Japanese robot industry. In 1991, Japan's robot production reached its first in history. The peak value of 600.3 billion yen; 1992-2000 is the stable development period of the Japanese robot industry, and in the late 1990s due to export pull, Japan appeared the second robot boom in history, and the shipment reached its second peak in 6475 in 2000. Billion Yen; Since 2001, due to the slow recovery of the Japanese economy and the sharp pull of exports, the industrial robotic boom in Japan has rebounded, and the shipment volume reached a record high of 730.3 billion yen in 2006.
In the process of continuous development and maturity of the industrial robot industry in Japan, along with the continuous integration of industries, the market concentration has increased and the number of enterprises has decreased. In Japan, the number of industrial robots in 1980 was 282, and by 2007 it was reduced to 108.
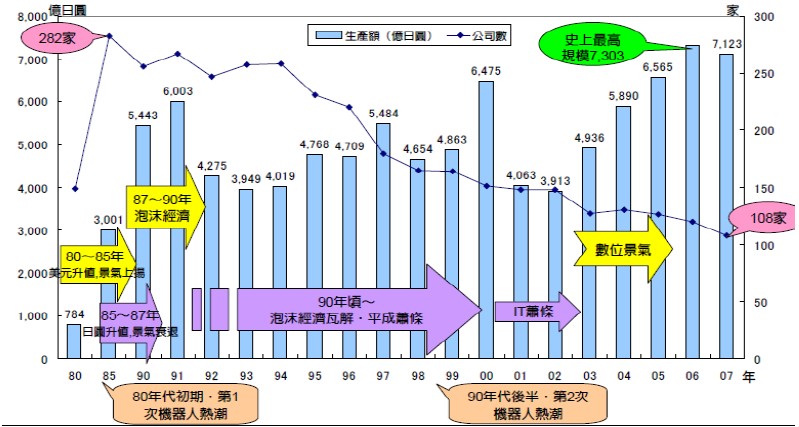
Figure 1: The development of the Japanese robot industry
Before the early 1980s, Japanese industrial robots were in the initial stage of explosive growth. In 1970, the output of industrial robots in Japan was 1,350 units. By 1980, the output was 19,843 units, the CAGR was at 30.84%, and the number of units increased from 1,000 units in 1974 to In the year of 1980, 14,250 units had a CAGR of 30.43%.
1980-1991 was the endogenous growth stage of Japanese industrial robots. Japan’s rapid economic growth around the 1980s, Japan’s domestic manufacturing labor force population shortage (the average annual growth rate of Japanese manufacturing employment: 3.30% in 1960-1973, 0.44% in 1973-1992, -2.47% in 1992-2002), Manufacturing wages have risen sharply. In this context, the Japanese government has actively adopted economic support policies to encourage the development and application of robots. On the other hand, it has further stimulated the enthusiasm of enterprises in the robot industry.
Figure 2: Japan's manufacturing wage index from 1952 to 2005 (2000 = 100)
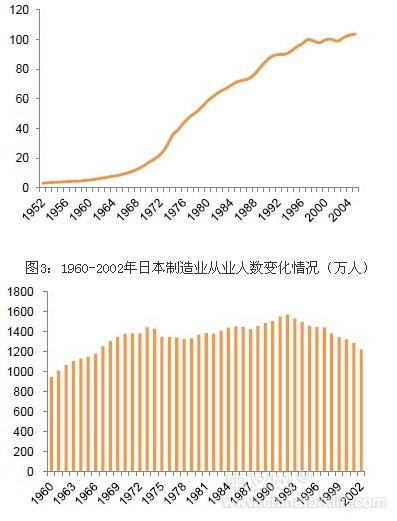
Therefore, during the 1980-1991 period, the Japanese robot industry grew rapidly. From 1980 to 1991, the Japanese industrial robot shipments increased from 78.4 billion yen to 600.3 billion yen, CAGR reached 20.33%, and the number of industrial robots was from 14,250 in 1980. Increased to 375,110 units in 1993, CAGR is in. During this period, the large-scale use of Japanese industrial robots solved the Japanese labor shortage, increased productivity, improved product quality and reduced production costs, and promoted and maintained Japan's economic growth rate and product competitiveness.
Rebar Bending Machine,Machine Tool Equipment,Cnc Steel Bar Bending Machines,Rebar Automatic Bending Machines
Xuchang Jingrui Machine Manufacturing Co., Ltd. , https://www.jingruisteelbarcutter.com
