How Does a Laser Cutting Machine Work?
I. Introduction
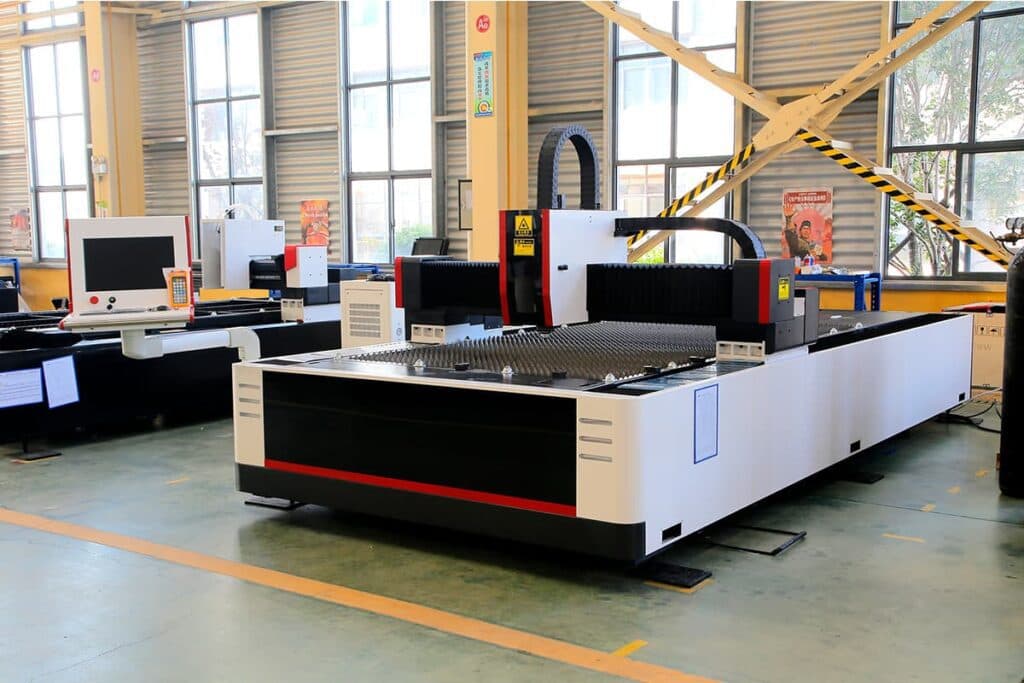
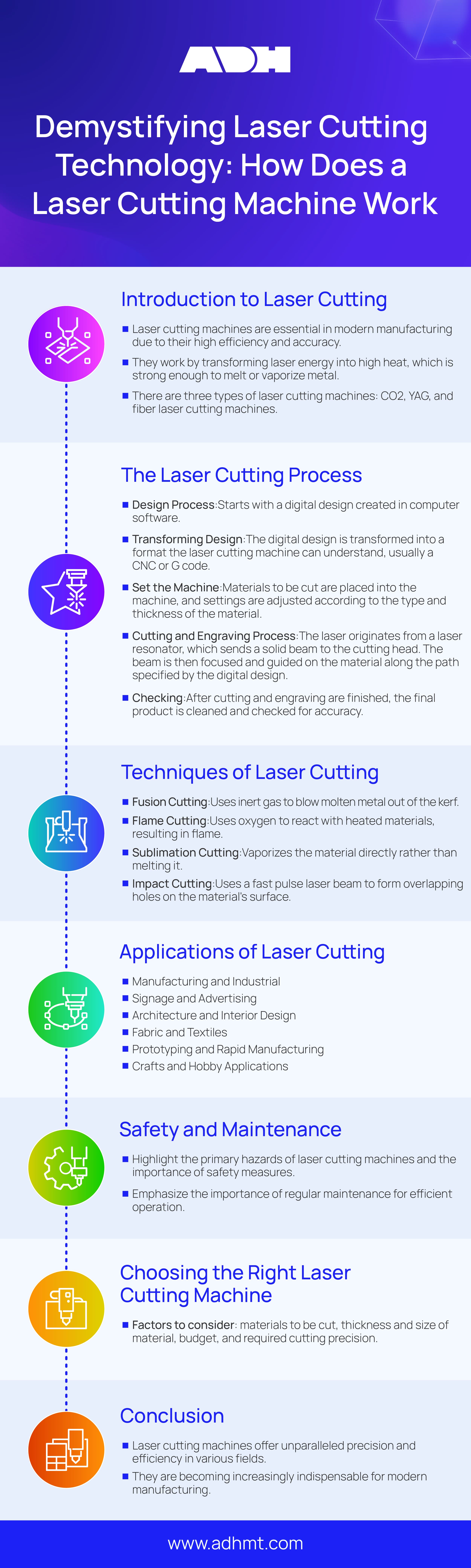
The laser cutting machine is an essential device for modern manufacture, which boosts high efficiency and accuracy and gives its high priority for metal fabrication.
So, how does a laser cutting machine work?
The laser-cutting machine transforms the laser energy into extremely high heat via a focusing laser beam.
This heat is strong enough to make metal melt or vaporize. When a laser beam passes through the materials, it will form a thin line on the surface of the metal.
The temperature of the line is high enough to cut the materials.
By manipulating the movement of the cutting head, the machine can finish the complex shapes cutting.
There are three kinds of laser cutting machines: CO2Â laser cutting machine, YAG laser cutting machine, and fiber laser cutting machine.
Despite different types, the working process of the laser cutting machine is still relatively the same.
Just start the cutting or engraving process according to the following simple steps:
II. Laser Cutting Process

Step 1 Design Process
This process starts with a digital design created in the computer software, which involves what the machine will cut or engrave.
Step 2 Transforming Design
Then transform the digital design into a format the laser cutting machine can understand.Â
This format is a file type usually called CNC (shortening the blade distance and improving productivity by decreasing the manufacturing time)or G code.
The G code is a group of machine-readable instructions that orders the machine to move the laser cutting head to somewhere.
The complex shapes require CAM (computer assistant manufacturing) software to generate G code automatically from the provided CAD (computer assistant design)file.
Send this G code to the controller of the laser cutting machine via a Wi-fi connection or USB driver.
After the design step, the next one is to set optimal parameters for the process.
Step 3 Set the Machine
Put the materials to be cut into the laser cutting machine, and adjust the location according to the types and thickness of the material.
This setting includes the power of the laser, the movement speed of the laser, and the focus of the laser beam.
The best optimal parameter depends on the model of the laser cutting machine and the types of materials being cut.
Step 4 Cutting and Engraving Process
After setting all the contents and beginning to operate, you can start the cutting and engraving.
It all begins with laser resource, which generates solid and consistent light.
The laser resource origins from a laser resonator, which sends a solid beam to the cutting head through the mirror system.
Inside the cutting head, the laser is focused by the lens and reduced to a skinny, concentrated beam.
This beam can be guided on the material along the path specified by digital to cut or raster the raw material.
By the way, if you use sunlight and a magnifying glass to start a fire, you will be more familiar with the working principle.
When the light moves along the path, it will melt, burn or vaporize the material, resulting in precise cutting and engraving.
The laser-cutting machine can also blow away the extra materials via a gas jet. The cutting head is usually fixed on the gantry, which is a mechanical system.
A belt or chain usually drives this system and allows for cutting head to move accurately in a specific rectangle region (the size of working bed).
The gantry allows the cutting head to move back and forth on the the workpiece to cut precisely at any place on the bed.
The laser should focus on the material being cut to achieve the best cutting state.
All the laser cutting machines need to focus the program before cutting to ensure an excellent laser-cutting effect.
Apart from the function of the laser itself, the laser cutting machine also is equipped with assistant gas.
This gas is jetted from the cutting head in the cutting process and assists in cooling the materials and cleaning the melted metals.
As a consequence, the laser cutting machine can not only provide accurate cutting but also can keep the cutting surface clean and smooth.
Step 5 Finally, Checking
After the material cutting and engraving are finished, if necessary, clean the finished product. Check out the accuracy and clear any debris.
III. Techniques of Laser Cutting
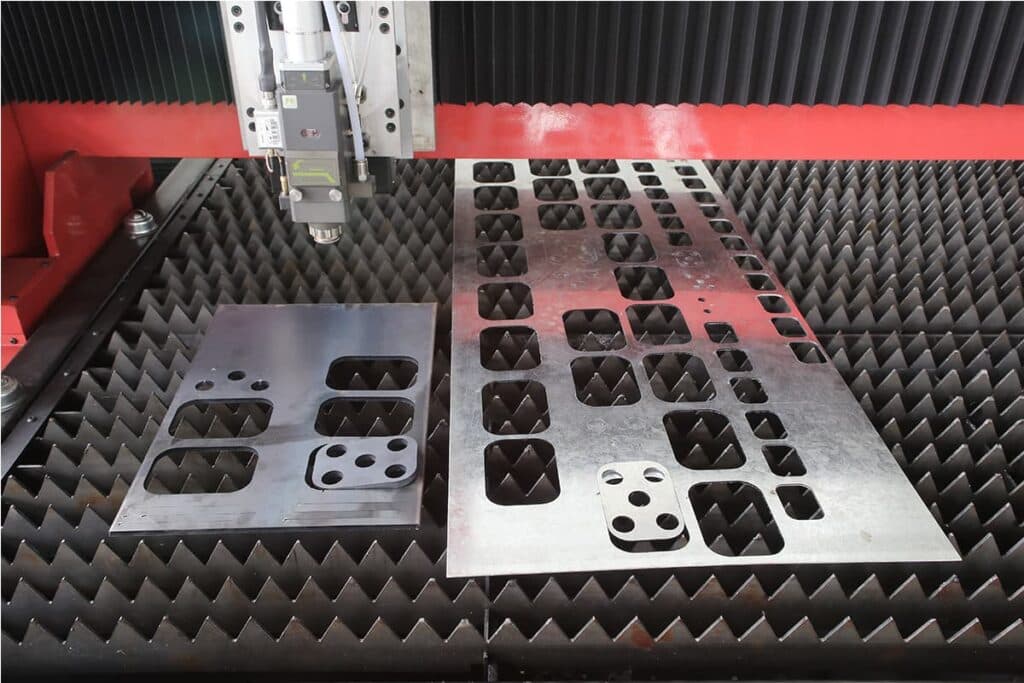

Based on the types of assistant gas, there are four different cutting techniques:
Fusion Cutting
In infusion cutting, the assistant gas does not assist in melting material but works only after the laser has melted the material.
Inert gas (nitrogen) is usually regarded as an assistant gas for cutting.
Pressurized assist gas blows molten metal out of the kerf, increasing the cutting speed and reducing the laser power required to cut material.
Fusion cutting is used for cutting metal. This technique is also named melting and blow cutting.
Flame Cutting
The assistant gas (oxygen) participates in the material’s burning and melting in flame cutting.
The laser beam heats the material, and oxygen reacts with heated materials, resulting in flame. This increases the power input to the material and benefits the laser beam in cutting material.
At the same time, I am using the high-pressure oxygen flow to blow away melted metal, thus realizing cutting.
Flame cutting is usually used for thick carbon steel materials.
Due to the reaction between oxygen and heated materials, this technique is also called reactive cutting.
Sublimation Cutting
Sublimation cutting will show up when thin materials (such as foils and fabrics) are cut under no assistant gas.
In this method, a laser beam vaporizes the material directly rather than melting it.
The high energy can evaporate the material on the focus, thus forming a narrow cut.
This kind of cutting is also called vaporization cutting.
Impact Cutting
Impact cutting is used for materials that are difficult to cut with continuous laser beams.
It involves a fast pulse laser beam on the material's surface to form overlapping holes.
Impact cutting usually is applied for cutting brittle materials such as ceramics and glass.
Different kinds of lasers should be based on the actual application and materials.
For example, the CO2 laser is usually used for cutting various materials, and the fiber laser is generally applied for metal.
The laser cutting machine utilizes the synergistic effect of high energy laser beam and assistant gas to fulfill the accuracy and high-efficiency cutting of metal materials.
Accepting training and knowledge when operating the laser cutting machine is vital. Thus safety and best results can be achieved.
Also, the machine requires regular maintenance to keep it working efficiently.
IV. What Is Laser Cutting Used For

The laser cutting machine is widely applied in many industries due to its accuracy, versatility, and ability to cut assorted materials. The following is an everyday use of laser cutting machines:
Manufacture and Industrial
The laser cutting machine is widely used in the process of manufacture to cut and shape various materials.
It creates complex designs, patterns, and components for automobiles, aerospace, electronics, and machinery.
Meanwhile, it can be applied to cut metal, plastic, rubber, wood, and composite materials.
Signage and Advertising
Laser cutting is prevalent in signage and advertising for creating custom signage, lettering, logos, and decorative elements.
It can precisely cut acrylic, wood, foam, and metal to produce intricate and visually appealing designs.
Architecture and Interior Design
Laser cutting is also widely used in architecture and interior design to create intricate patterns, decorative panels, screens, and partitions.
It can operate precise and intricate cutting of wood, acrylic, glass, and metal, thus realizing unique and custom architectural elements.
Fabric and Textiles
Laser cutting is used in the textile and fashion industries for fabric, leather, and other materials used in clothing production.
It offers precise and clean cuts, complex patterns, and the ability to quickly create intricate designs, making it an invaluable tool in the fashion industry.
Prototyping and Rapid Manufacturing
Laser cutting is used in prototyping and rapid manufacturing for quickly producing prototypes, running small production, and customizing parts.
Its speed, accuracy, and ability to handle various materials make it an ideal technology for rapid prototyping and iterative design processes.
Crafts and Hobby Applications
Laser cutting is popular among hobbyists, artists, and crafts enthusiasts.
It can cut and engrave materials precisely, such as wood, paper, acrylic, and leather, to create intricate designs, jewelry, ornaments, and personalized gifts.
V. Conclusion
The laser cutting machine adopts high-power lasers to cut accurately and efficiently in many fields.
Various cutting techniques, such as flame and fusion, are becoming increasingly indispensable for modern manufacturing and manufacturing.
ADH's laser cutting machines offer unparalleled precision and efficiency in metalworking, sheet metal fabrication, and various mechanical engineering applications.
Act now and transform your production process today!
You can browse our products to choose the suitable machine or consult our sales to learn detailed information.
Click on the link to download high-definition images.
Coating Machinery,Bottom Spray Coater,Pharmaceutical Coating Machine,Tablet Film Coating Machine
Changzhou Bole Tech Co.,Ltd , https://www.boledrying.com
