Metals Institute made flexible carbon nanotube sensing and storage integrated device
[ Instrument Network R & D ] Charge-coupled device (CCD) and charge-storage device (Memory) as two independent branches in modern electronic systems have developed along their respective paths, and prototype devices with photoelectric sensing and storage functions have not been reported yet . Recently, researchers from the Shenyang National Research Center for Materials Science, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences have collaborated with many domestic institutions to publish an online article entitled "Flexible Carbon Nanotube Sensor-Storage Device" on Advanced Materials nanotube sen-memory device).
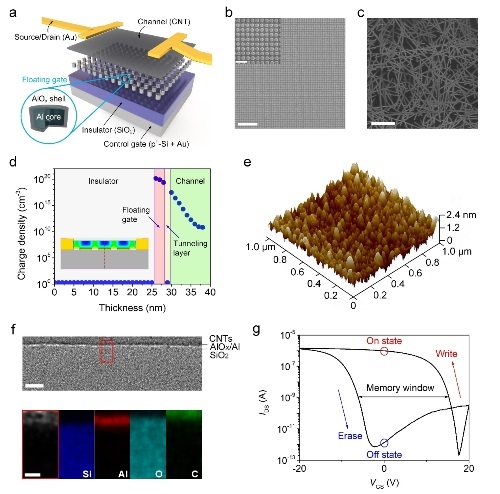
Researchers have proposed a carbon nanotube non-volatile memory based on aluminum nanocrystalline floating gates. It has a high current switching ratio, a storage time of up to 10 years, and stable read and write operations. Multiple discrete aluminum nanocrystals Floating gate devices have stable and flexible performance. More importantly, the tunneling mechanism of charges in the AlOx layer formed by oxidation changed from Fowler-Nordheim tunneling to direct tunneling, so as to realize the sensing and detection of photoelectric signals; based on theoretical calculation analysis and experimental optimization Designed and prepared a 32 × 32 pixel non-volatile flexible ultraviolet area array device, realized the optical image sensing and image storage for the first time, and laid the foundation for the development of new flexible light detection and storage devices.
Carbon nanotubes, as one-dimensional nanomaterials, are lightweight and have a hexagonal structure with perfect connections. They have many unusual mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. In recent years, with the research of carbon nanotubes and nanomaterials, its broad application prospects have been continuously shown.
Carbon nanotubes, also known as bucky tubes, are one-dimensional quantum materials with special structures (radial dimensions are on the order of nanometers, axial dimensions are on the order of micrometers, and both ends of the tube are basically sealed). Carbon nanotubes are mainly composed of carbon atoms arranged in hexagons. A fixed distance is maintained between the layers, about 0.34 nm, and the diameter is generally 2-20 nm. And according to the different orientations of the carbon hexagon in the axial direction, it can be divided into three types: zigzag, armchair and spiral. The spiral carbon nanotubes have chirality, while the zigzag and armchair carbon nanotubes have no chirality.
Researchers use semiconductor carbon nanotube films as channel materials, and use uniformly and discretely distributed aluminum nanocrystal / alumina integrated structures as floating gate layers and tunneling layers to obtain high-performance flexible carbon nanotube floating gate memories. Under 0.4% bending strain, the current switching ratio between read and write and erase of the device is higher than 105, and the storage stability is more than 108s. At the same time, the thinner aluminum oxide tunneling layer allows the carriers in the erased state to “entrain†the aluminum nanocrystalline floating gate to return to the channel by direct tunneling when the light energy is higher than the aluminum work function. Among them, the off-state current has been significantly improved, the direct conversion and transmission of photoelectric signals are completed, and a new type of multi-functional photoelectric sensing and storage system integrating image sensing and information storage is realized.
A photoelectric sensor is a device that converts light signals into electrical signals. Its working principle is based on the photoelectric effect. Photoelectric effect refers to the phenomenon that when the light is irradiated on certain substances, the electrons of the substances absorb the energy of the photons and the corresponding electric effect occurs. According to the different photoelectric effect phenomena, the photoelectric effect is divided into three categories: external photoelectric effect, internal photoelectric effect and photovoltaic effect. Photoelectric devices include photocells, photomultiplier tubes, photoresistors, photodiodes, phototransistors, and photovoltaic cells. The performance and characteristic curves of photovoltaic devices are analyzed.
The research work was proposed by Sun Dongming and Qu Tingyu of the Institute of Metals, and was completed in cooperation with Qiu Song and Li Qingwen, researchers of the Institute of Nanotechnology and Nanobionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Professor Wang Wei of Jilin University, and researchers from the Institute of Metals. Qu Tingyu and Sun Meteor carried out device preparation, electrical measurement, and data analysis work. Chen Maolin conducted device process research such as electron beam exposure. Qiu Song and Li Qingwen synthesized semiconductor carbon nanotube solutions, and Liu Zhibo performed transmission electron microscopy of the samples. Characterization, Tan Jun carried out sample processing such as focused ion beam. All authors participated in data analysis discussions and thesis writing. Qu Tingyu, Sun Meteor, and Chen Maolin are co-first authors, and Qiu Song, Han Zheng, Cheng Huiming, and Sun Dongming are co-corresponding authors. This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Metals, the National Research Center for Materials Science, the Thousand Talents Program, and the National Key R & D Program.
Source: Encyclopedia, Metal Research Institute
Vacuum Mixer Dryer,Rotary Vacuum Dryer,Industrial Vacuum Dryer,U Shape Mixing Vacuum Dryer
WUXI ZHANGHUA PHARMACEUTICAL EQUIPMENT CO., LTD. , https://www.filterdryer1976.com
